Difference between revisions of "Bolton IVC Plant"
(Created page with "==Article in NCE Special Report – Structural Steelwork in action, 08/11/12== {{#image_template:image=File:Bolton_IVC_Plant.png|caption=Borde...") |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
''By Martin Cooper''<br> | ''By Martin Cooper''<br> | ||
| − | The Greater Manchester Waste PFI scheme is the largest of its kind in Europe and steel framed buildings are crucial to the programme. | + | The Greater Manchester Waste PFI scheme is the largest of its kind in Europe and steel framed buildings are crucial to the programme. Worth £3.8bn, the Greater Manchester Waste scheme includes the construction of 42 recycling plants for household and industrial waste in and around the UK’s third largest conurbation. The overall programme is the largest such PFI in Europe and part of it includes the building of four In Vessel Composting (IVC) plants, designed by TEG Environmental, a specialist technology provider that designs, builds and operates sites that treat organic waste. |
| − | + | Many local authorities are now investing in IVC plants as they offer an environmentally friendly solution for recycling food and green household waste. This completely natural composting process generally takes approximately two weeks, with a further six to eight weeks for the product to stabilise before being dispatched as fertilizer. | |
| − | The | + | The Bolton plant is the fourth IVC facility to be constructed by TEG in the PFI scheme, following on from similar builds in Rochdale, Bredbury and Trafford Park. “Together the plants will recycle 179,000t of organic waste per annum, Bolton IVC will deliver 50,000t of this total,” says TEG contract manager Nichola Rafferty. |
| − | + | All of the IVC facilities are housed within steel framed structures and Border Steelwork Structures has [[Construction#Steel erection|erected]] three of these projects on behalf of TEG. “[[The_case_for_steel|Cost, efficiency and the need for large clear spans]] were the main reasons why the IVC plants are all steel framed structures,” explains Thomas Jagger, a director at project architect TD Jagger. | |
| − | + | For the Bolton plant, Border has [[Construction#Steel erection|erected]] 340t of structural steelwork as part of its overall contract as [[Building_envelopes|envelope]] provider. “We are responsible for all internal civil works,” says Border Steelwork Structures senior contracts manager Stuart Airey. “As the steelwork fabricator, supplier and erector, it has been beneficial for us to also take responsibility for the civil and building elements as well as the [[Building_envelopes#Types of metal cladding systems|cladding]] and roofing of the plant, as all of these trades revolve around the completion of the [[Portal_frames|steel frame]].” | |
| − | + | Border started on this former British Coal site, located on the outskirts of Bolton, last February. Previously Costain had completed a thorough ground improvement programme as a number of mine workings beneath the site needed to be drilled and grouted. The ground was then stabilised, vibro stone columns installed and ground beams cast. Following the completion of the foundation works, the [[Construction#Steel erection|steel erection]] programme started in May and this process was divided into three phases in order to complete the task as quickly as possible. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Border started on this former British Coal site, located on the outskirts of Bolton, last February. Previously Costain had completed a thorough ground improvement programme as a number of mine workings beneath the site needed to be drilled and grouted. | ||
| − | |||
| − | The ground was then stabilised, vibro stone columns installed and ground beams cast. | ||
| − | |||
| − | Following the completion of the foundation works, the [[Construction#Steel erection|steel erection]] programme started in May and this process was divided into three phases in order to complete the task as quickly as possible | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{#image_template:image=File:Bolton-2.png|caption=In Vessel Composting (IVC) Process|align=left|wrap=true|width=400}} | {{#image_template:image=File:Bolton-2.png|caption=In Vessel Composting (IVC) Process|align=left|wrap=true|width=400}} | ||
| − | The first part houses the waste intake area with bunkers and shredding equipment; the second contains the composting technology and the third is the compost management building where compost is stored while it stabilises | + | The overall footprint of the structure is 8,046m<sup>2</sup> and measures 96m by 84m. For operational purposes the building is split into three distinct parts to comply with industry regulations, which require designated “clean” and “dirty” areas of operation to avoid cross contamination between the waste and the finished product. The first part houses the waste intake area with bunkers and shredding equipment; the second contains the composting technology and the third is the compost management building where compost is stored while it stabilises. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | “The requirement for three distinct zones dictated the [[Design|structural design]] of the plant,” says Jagger. “We had to devise a way these could all be accommodated within a structure with no strange shapes; a [[Design#Portal frames|steel portal design]] was the best option.” Long clear spans are important, as the waste intake area will have numerous vehicles manoeuvring. Internal columns, which could hinder vehicle movement, were out of the question, so a clear span 30m [[Portal_frames|portal frame]] has been erected. Interestingly, this part of the structure has been swivelled 90° from the rest of the steel frame in order to get the long clear spans. The building is 48m wide in the opposite direction and this was deemed too long for a single span. | |
| − | + | The zone directly behind the waste intake area, which houses the composting technology, is facing in the other direction and the 48m width is accommodated with a [[Portal_frames#Types of portal frames|propped portal frame]]. The three column bays measure 18m, 12m and 18m, and accommodate the three silo cage composting lines. “We erected the steelwork]] for the area to house the composting lines first, followed by the waste intake area, to enable TEG’s specialist suppliers to proceed as quickly as possible,” says Airey. “It was important to get the steelwork up to allow the job to progress steadily.” | |
{{#image_template:image=File:Bolton-1.png|caption=Long spans were important|align=right|wrap=true|width=300}} | {{#image_template:image=File:Bolton-1.png|caption=Long spans were important|align=right|wrap=true|width=300}} | ||
| − | Immediately after the steel frame was erected the [[Building_envelopes|cladding]] and roofing contractors followed on behind, ensuring the structure was watertight as quickly as possible. | + | While [[Construction#Steel erection|steelwork erection]] was ongoing in one phase, bunkers and plinths for the silo cages were being cast simultaneously in adjacent zones. As Border was responsible for the entire package, it could organise all trades around one common roster. Immediately after the steel frame was erected the [[Building_envelopes|cladding]] and roofing contractors followed on behind, ensuring the structure was watertight as quickly as possible. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Construction]] of | + | For the [[Construction#Steel erection|steel erection]] programme, Border used a 50t capacity [[Construction#Mobile cranes|mobile crane]], while a mobile tower crane was utilised to [[Building_envelopes#Building envelope installation|install the cladding]]. The building’s [[Building_envelopes|cladding]] consists of a traditional [[Building_envelopes#Insulated_.28composite_or_sandwich.29_panels|composite panel]] with a 200 micron thick external [[Paint_coatings|paint coating]], which is applied internally as well as externally to protect it from the humid composting environment |
| − | TEG site manager David Nicholson says: “The project is going well, the build is on programme and we expect to be commissioning the plant early next year. | + | [[Construction]] of the Bolton IVC is due for completion in March 2013 and the plant will start receiving waste in April 2013. TEG will remain on site during the commissioning phase, to oversee the operation and train the Viridor staff, who will ultimately be running the site. TEG site manager David Nicholson says: “The project is going well, the build is on programme and we expect to be commissioning the plant early next year. |
{|class="wikitable" width=400 | {|class="wikitable" width=400 | ||
Revision as of 12:13, 12 March 2019
Article in NCE Special Report – Structural Steelwork in action, 08/11/12
Organic household waste solution
By Martin Cooper
The Greater Manchester Waste PFI scheme is the largest of its kind in Europe and steel framed buildings are crucial to the programme. Worth £3.8bn, the Greater Manchester Waste scheme includes the construction of 42 recycling plants for household and industrial waste in and around the UK’s third largest conurbation. The overall programme is the largest such PFI in Europe and part of it includes the building of four In Vessel Composting (IVC) plants, designed by TEG Environmental, a specialist technology provider that designs, builds and operates sites that treat organic waste.
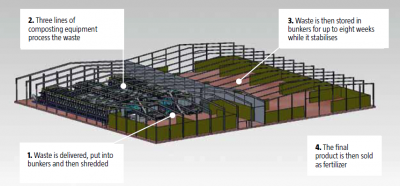
Many local authorities are now investing in IVC plants as they offer an environmentally friendly solution for recycling food and green household waste. This completely natural composting process generally takes approximately two weeks, with a further six to eight weeks for the product to stabilise before being dispatched as fertilizer.
The Bolton plant is the fourth IVC facility to be constructed by TEG in the PFI scheme, following on from similar builds in Rochdale, Bredbury and Trafford Park. “Together the plants will recycle 179,000t of organic waste per annum, Bolton IVC will deliver 50,000t of this total,” says TEG contract manager Nichola Rafferty.
All of the IVC facilities are housed within steel framed structures and Border Steelwork Structures has erected three of these projects on behalf of TEG. “Cost, efficiency and the need for large clear spans were the main reasons why the IVC plants are all steel framed structures,” explains Thomas Jagger, a director at project architect TD Jagger.
For the Bolton plant, Border has erected 340t of structural steelwork as part of its overall contract as envelope provider. “We are responsible for all internal civil works,” says Border Steelwork Structures senior contracts manager Stuart Airey. “As the steelwork fabricator, supplier and erector, it has been beneficial for us to also take responsibility for the civil and building elements as well as the cladding and roofing of the plant, as all of these trades revolve around the completion of the steel frame.”
Border started on this former British Coal site, located on the outskirts of Bolton, last February. Previously Costain had completed a thorough ground improvement programme as a number of mine workings beneath the site needed to be drilled and grouted. The ground was then stabilised, vibro stone columns installed and ground beams cast. Following the completion of the foundation works, the steel erection programme started in May and this process was divided into three phases in order to complete the task as quickly as possible.
The overall footprint of the structure is 8,046m2 and measures 96m by 84m. For operational purposes the building is split into three distinct parts to comply with industry regulations, which require designated “clean” and “dirty” areas of operation to avoid cross contamination between the waste and the finished product. The first part houses the waste intake area with bunkers and shredding equipment; the second contains the composting technology and the third is the compost management building where compost is stored while it stabilises.
“The requirement for three distinct zones dictated the structural design of the plant,” says Jagger. “We had to devise a way these could all be accommodated within a structure with no strange shapes; a steel portal design was the best option.” Long clear spans are important, as the waste intake area will have numerous vehicles manoeuvring. Internal columns, which could hinder vehicle movement, were out of the question, so a clear span 30m portal frame has been erected. Interestingly, this part of the structure has been swivelled 90° from the rest of the steel frame in order to get the long clear spans. The building is 48m wide in the opposite direction and this was deemed too long for a single span.
The zone directly behind the waste intake area, which houses the composting technology, is facing in the other direction and the 48m width is accommodated with a propped portal frame. The three column bays measure 18m, 12m and 18m, and accommodate the three silo cage composting lines. “We erected the steelwork]] for the area to house the composting lines first, followed by the waste intake area, to enable TEG’s specialist suppliers to proceed as quickly as possible,” says Airey. “It was important to get the steelwork up to allow the job to progress steadily.”
While steelwork erection was ongoing in one phase, bunkers and plinths for the silo cages were being cast simultaneously in adjacent zones. As Border was responsible for the entire package, it could organise all trades around one common roster. Immediately after the steel frame was erected the cladding and roofing contractors followed on behind, ensuring the structure was watertight as quickly as possible.
For the steel erection programme, Border used a 50t capacity mobile crane, while a mobile tower crane was utilised to install the cladding. The building’s cladding consists of a traditional composite panel with a 200 micron thick external paint coating, which is applied internally as well as externally to protect it from the humid composting environment
Construction of the Bolton IVC is due for completion in March 2013 and the plant will start receiving waste in April 2013. TEG will remain on site during the commissioning phase, to oversee the operation and train the Viridor staff, who will ultimately be running the site. TEG site manager David Nicholson says: “The project is going well, the build is on programme and we expect to be commissioning the plant early next year.
| Architect | TD Jagger |
| Structural Engineer | AL Daines & Partners |
| Steelwork Contractor | Border Steelwork Structures |
| Main Contractor | Costain Construction |
| Client | Greater Manchester Waste Disposal Authority |
| Plant Operator | Viridor |
| Technology Provider | TEG Environmental |