Difference between revisions of "Fire and steel construction"
| (49 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__SECTIONLINKTOTOP__ | __SECTIONLINKTOTOP__ | ||
| − | + | Structural performance in the fire condition is an important design consideration for all materials. The strength of steel reduces at elevated temperatures, so structural steelwork will generally need protection if the resistance of an unprotected member cannot be justified. Fire protection materials have been developed over many years to provide an effective solution. In parallel, much research has been undertaken into the performance of members and buildings at elevated temperatures, leading to comprehensive design rules such as BS 5950-8<ref name="No9"> BS 5950-8: 2003, Structural use of steelwork in buildings. Code of practice for fire resistant design. BSI</ref> and BS EN 1993-1-2<ref name="No11">BS EN 1993-1-2: 2005, Design of steel structures. General rules - structural fire design. BSI</ref> | |
| + | |||
| + | A [[#Resources|2024 update]] on the fire performance and fire protection of structural steelwork gives a high-level overview for clients and their design teams. This summary makes particular reference to the Regulatory changes being introduced under the 2022 Building Safety Act. | ||
<gallery caption="Structural fire engineering case studies" wrap=true style="float:right;" perrow=3 widths=200px heights=230px> | <gallery caption="Structural fire engineering case studies" wrap=true style="float:right;" perrow=3 widths=200px heights=230px> | ||
Image:Dypatil_school_of_management.png|[[External_steel_at_the_D_Y_Patil_School_of_Management|External steel at the D. Y. Patil School of Management]] | Image:Dypatil_school_of_management.png|[[External_steel_at_the_D_Y_Patil_School_of_Management|External steel at the D. Y. Patil School of Management]] | ||
| Line 7: | Line 9: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==The Building Regulations and fire precautions in buildings== | ==The Building Regulations and fire precautions in buildings== | ||
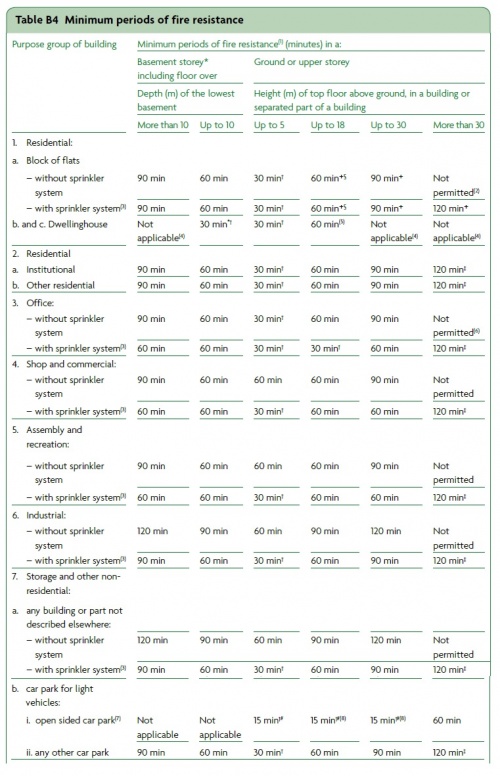
| − | {{#image_template:image=File:Table_B4.jpg|caption=Structural fire resistance requirements for non-residential buildings in [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2">[https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/ | + | {{#image_template:image=File:Table_B4.jpg|caption=Structural fire resistance requirements for non-residential buildings in [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2">[https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/937932/ADB_Vol2_Buildings_other_than_dwellings_2019_edition_inc_2020_amendments.pdf Approved Document B (Fire safety, Volume 2 – Buildings other than Dwellings), 2019 edition incorporating 2020 amendments – for use in England . Ministry of Housing, Communities & Local Government]</ref>|align=right|wrap=true|width=500}} |
''Main articles: [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|Structural fire resistance requirements]]'' | ''Main articles: [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|Structural fire resistance requirements]]'' | ||
| − | The obligations placed on those who design and construct buildings to ensure that they are both safe and healthy are contained in the Building Regulations. The requirements of the regulations are set out in functional terms, i.e. they outline what | + | The obligations placed on those who design and construct buildings to ensure that they are both safe and healthy are contained in the Building Regulations. The requirements of the regulations are set out in functional terms, i.e. they outline what must be achieved, but do not prescribe how the requirements are to be satisfied. |
For example, Requirement B3(1) of the Building Regulations for England states that ''The building shall be designed and constructed so that, in the event of a fire, its stability will be maintained for a reasonable period''. The equivalent requirement (2.3) in the Scottish Building Regulations states that ''Every building must be designed and constructed in such a way that in the event of an outbreak of fire within the building, the load-bearing capacity of the building will continue to function until all occupants have escaped, or been assisted to escape, from the building and any fire containment measures have been initiated''. | For example, Requirement B3(1) of the Building Regulations for England states that ''The building shall be designed and constructed so that, in the event of a fire, its stability will be maintained for a reasonable period''. The equivalent requirement (2.3) in the Scottish Building Regulations states that ''Every building must be designed and constructed in such a way that in the event of an outbreak of fire within the building, the load-bearing capacity of the building will continue to function until all occupants have escaped, or been assisted to escape, from the building and any fire containment measures have been initiated''. | ||
| − | The Governments of the various regions of the UK publish documents which provide guidance on means by which compliance can be achieved. In terms of fire, the most widely used of these is England's [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref>. Amongst the various rules for fire safety in buildings contained in this document are details of the [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|structural fire resistance requirements]] to meet the obligations for structural stability described above. For example, an office building over 30 metres in height requires 120 minutes [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|fire resistance]] plus a [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes|life safety sprinkler]] system | + | The Governments of the various regions of the UK publish documents which provide guidance on means by which compliance can be achieved. In terms of fire, the most widely used of these is England's [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref>. Amongst the various rules for fire safety in buildings contained in this document are details of the [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|structural fire resistance requirements]] to meet the obligations for structural stability described above. For example, an office building over 30 metres in height requires 120 minutes [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|fire resistance]] plus a [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes|life safety sprinkler]] system. An assembly building between 18 and 30 metres in height requires 90 minutes [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|fire resistance]], unless it has a sprinkler system when the fire resistance period reduces to 60 minutes. Until April 2014, this document was shared between England & Wales but in that month, a separate document was issued for Wales<ref name="No18">[https://gov.wales/sites/default/files/publications/2021-12/building-regulations-guidance-part-b-fire-safety-volume-2-buildings-other-than-dwellinghouses.pdf Approved Document B, Volume 2 – Buildings other than dwellinghouses, Fire safety, 2006 Edition incorporating 2010, 2013, 2016, 2017 and 2020 amendments - For use in Wales*, Welsh Government]</ref>. The differences between these are small but it is necessary to know that they exist. |
<gallery widths=180px heights=255px> | <gallery widths=180px heights=255px> | ||
Image:Approved_Document_B_cover.png|[[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> | Image:Approved_Document_B_cover.png|[[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> | ||
Image:Welsh_Approved_Document_B.png|Welsh Approved Document B<ref name="No18"></ref> | Image:Welsh_Approved_Document_B.png|Welsh Approved Document B<ref name="No18"></ref> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | In Scotland the equivalent document is [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements# | + | In Scotland the equivalent document is [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Technical_Handbook_2022|Scottish Technical Handbook 2022]]<ref name="No3">[https://www.gov.scot/publications/building-standards-2022-technical-handbook-non-domestic/ Building standards technical handbook: 2022 – Non-domestic, Section 2 – Fire, The Scottish Government]</ref> and in Northern Ireland it is [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Technical_Booklet_E|Technical Booklet E]]<ref name="No4">[https://www.finance-ni.gov.uk/sites/default/files/publications/dfp/Technical-booklet-E-Fire-Safety-October-2012_0.pdf Technical Booklet E, Fire safety, Building Regulations (Northern Ireland) 2012, Department of Finance and Personnel of the Northern Ireland Government, 2012]</ref>. Some [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Local_and_building_specific_regulations|local and building specific regulations]] are also in place. |
<gallery widths=180px heights=255px> | <gallery widths=180px heights=255px> | ||
Image:Technical_Booklet_E_2012.png|[[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Technical_Booklet_E|Technical Booklet E]]<ref name="No4"></ref> | Image:Technical_Booklet_E_2012.png|[[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Technical_Booklet_E|Technical Booklet E]]<ref name="No4"></ref> | ||
Image:BS9999_front_cover.png|[[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#BS_9999|BS 9999]]<ref name="No5"></ref> Code of practice for fire safety in the design, use and management of buildings | Image:BS9999_front_cover.png|[[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#BS_9999|BS 9999]]<ref name="No5"></ref> Code of practice for fire safety in the design, use and management of buildings | ||
</gallery><br> | </gallery><br> | ||
| − | All the Government documents provide provision for alternative solutions using [[Fire_and_steel_construction#Structural_fire_engineering|fire safety engineering]] approaches. [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> states that ''[[Structural_fire_engineering|Fire safety engineering]] | + | All the Government documents provide provision for alternative solutions using [[Fire_and_steel_construction#Structural_fire_engineering|fire safety engineering]] approaches. [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> paragraph 0.18 states that ''[[Structural_fire_engineering|Fire safety engineering]] might provide an alternative approach to fire safety. Fire safety engineering may be the only practical way to achieve a satisfactory standard of fire safety in some complex buildings and buildings that contain different uses''. |
| − | In recent years, as the result of extensive research into the nature of fire, how it spreads and the risk factors in building fires, the British Standards Institute has published [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#BS_9999|BS 9999]]<ref name="No5">BS 9999: 2017, Fire safety in the design, management and use of buildings - Code of practice. BSI</ref>. The intention behind the development of the document is to provide a more transparent and flexible approach to fire safe design through the use of a structured approach to risk | + | In recent years, as the result of extensive research into the nature of fire, how it spreads and the risk factors in building fires, the British Standards Institute has published [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#BS_9999|BS 9999]]<ref name="No5">BS 9999: 2017, Fire safety in the design, management and use of buildings - Code of practice. BSI</ref>. The intention behind the development of the document is to provide a more transparent and flexible approach to fire safe design through the use of a structured approach to risk. |
<br clear=right> | <br clear=right> | ||
| Line 33: | Line 35: | ||
''Main articles: [[Fire_testing|Fire testing]], [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards|Design using structural fire standards]]'' | ''Main articles: [[Fire_testing|Fire testing]], [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards|Design using structural fire standards]]'' | ||
| − | All [[Steel_construction_products#Standard_open_sections| | + | All [[Steel_construction_products#Standard_open_sections|structural steel sections]] have some inherent fire resistance and this is a function of the size of the section, its degree of exposure to the fire and the load that it carries. |
| − | |||
| − | The | + | The fire resistance of an element is usually defined as the time for which the element can satisfy appropriate criteria (for example, its load-carrying resistance). Tests are undertaken in a furnace where the temperature follows a standard time-temperature relationship as shown, which is the same for all materials. The standard time-temperature curve does not follow the general behaviour in a real fire, where the temperature falls once the fire load (matter which burns) has been consumed. The fire resistance periods obtained in a test are a measure of the adequacy of the construction in a fire but have no direct relationship with the duration of a real fire. BS 476-20<ref name="No6"> BS 476-20: 1987, Fire tests on building materials and structures. Method for determination of the fire resistance of elements of construction (general principles). BSI</ref>, ISO 834<ref name="No7"> ISO 834-1: 1999, Fire-resistance tests - Elements of building construction. General requirements. International Standards Organisation</ref> and BS EN 1363-1<ref name="No8"> BS EN 1363-1: 2020, Fire resistance tests. General requirements . BSI</ref> describe the standard test. |
| − | For small, fully loaded [[Steel_construction_products#Standard_open_sections| | + | The strength of [[Steel_construction_products#Standard_open_sections|structural steel]] decreases with temperature. Following an extensive series of [[Fire_testing#The_standard_fire_test|standard fire tests]], that [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Steelwork_strength_in_fire|strength reduction]] has been quantified. Recent international research has also shown that the [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Steelwork_strength_in_fire|limiting (failure) temperature]] of a structural steel member is not fixed but varies according to two factors, the [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Effect_of_temperature_profile|temperature profile]] through the cross section and the design [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Effect_of_load|load]]. |
| + | |||
| + | For small, fully loaded [[Steel_construction_products#Standard_open_sections|sections]], exposed on all four sides, the inherent fire resistance without added [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|protection]] can be as little as 12 minutes. For very large [[Steel_construction_products#Standard_open_sections|sections]], lightly loaded and with some partial protection from concrete floor slabs on the upper flange, this can be as high as 50 minutes. Where the heated perimeter is further reduced by the method of the construction (e.g. [[Floor_systems#Shallow floors|shallow floor systems]]), up to 60 minutes inherent fire resistance can be achieved. [[#Resources|SCI-P186]] describes methods of designing steel framed buildings for 30 and 60 minutes fire resistance without applied fire protection. | ||
<gallery widths=300px heights=170px> | <gallery widths=300px heights=170px> | ||
Image:Standard_fire_test.png| The [[Fire_testing#The_standard_fire_test|standard fire test]] time-temperature relationship | Image:Standard_fire_test.png| The [[Fire_testing#The_standard_fire_test|standard fire test]] time-temperature relationship | ||
| Line 44: | Line 47: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | Where the inherent fire resistance of the steel is less than that necessary to meet the requirements for structural stability for the building, additional precautions must be taken. This usually takes the form of applied [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|fire protection]] which insulates the steel from the increasing temperatures. | + | Where the inherent fire resistance of the steel is less than that necessary to meet the requirements for structural stability for the building, additional precautions must be taken. This usually takes the form of applied [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|fire protection]] which insulates the steel from the increasing temperatures. The fire resistance of [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|hollow sections]] may be increased by [[Fire_and_steel_construction#Hollow_sections_in_fire|concrete filling]], which may mean that external [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|fire protection]] is not required. |
==Design using structural fire standards== | ==Design using structural fire standards== | ||
| Line 50: | Line 53: | ||
''Main articles: [[Fire_testing|Fire testing]], [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards|Design using structural fire standards]],[[Structural_fire_engineering|Structural fire engineering]]'' | ''Main articles: [[Fire_testing|Fire testing]], [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards|Design using structural fire standards]],[[Structural_fire_engineering|Structural fire engineering]]'' | ||
| − | The world’s first design code for steel in fire, [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#BS5950_Part_8| | + | The world’s first design code for steel in fire, [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#BS5950_Part_8|BS 5950 Part 8]]<ref name="No9"></ref> was published in the UK in 1990 and redrafted in 2003. It is based on extensive testing by Tata Steel and the Building Research Establishment (BRE) and brings together in one document details of many of the methods of achieving fire resistance for structural steelwork. Although it is based on evaluation of performance of structural steel members in the [[Fire_testing#The_standard_fire_test|standard fire test]], it may also be used in [[Fire_and_steel_construction#Structural_fire_engineering|fire engineering]] assessments when [[Structural_fire_engineering#Parametric_time-temperature_relationships|parametric fire]] temperatures are derived by calculation. |
[[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#BS5950_Part_8|BS5950 Part 8]]<ref name="No9"></ref> also includes design information and guidance for design of [[Portal_frames|portal frames]], [[Fire_and_steel_construction#Hollow_sections_in_fire|hollow sections in fire]], [[Fire_and_steel_construction#External_steelwork_in_fire|external steelwork]], [[Fire_and_steel_construction#Composite_steel_deck_floors_in_fire|composite slabs]] and calculation of [[Fire_and_steel_construction#Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|fire protection]] thicknesses based on [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Steelwork_strength_in_fire|limiting (failure) temperatures]]. Background to the standard and worked examples (to the 1990 version) are given in [[#Resources|SCI P080]]. | [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#BS5950_Part_8|BS5950 Part 8]]<ref name="No9"></ref> also includes design information and guidance for design of [[Portal_frames|portal frames]], [[Fire_and_steel_construction#Hollow_sections_in_fire|hollow sections in fire]], [[Fire_and_steel_construction#External_steelwork_in_fire|external steelwork]], [[Fire_and_steel_construction#Composite_steel_deck_floors_in_fire|composite slabs]] and calculation of [[Fire_and_steel_construction#Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|fire protection]] thicknesses based on [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Steelwork_strength_in_fire|limiting (failure) temperatures]]. Background to the standard and worked examples (to the 1990 version) are given in [[#Resources|SCI P080]]. | ||
| − | The following [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Fire_Eurocodes|Eurocodes]] | + | The following [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Fire_Eurocodes|Eurocodes]] describe the rules for the fire design of buildings using structural steelwork: |
*BS EN 1991-1-2<ref name="No10">BS EN 1991-1-2: 2002, Actions on Structures. General actions - Actions on structures exposed to fire. BSI</ref>, | *BS EN 1991-1-2<ref name="No10">BS EN 1991-1-2: 2002, Actions on Structures. General actions - Actions on structures exposed to fire. BSI</ref>, | ||
| − | *BS EN 1993-1-2<ref name="No11"> | + | *BS EN 1993-1-2<ref name="No11"></ref> |
*BS EN 1994-1-2<ref name="No12">BS EN 1994-1-2: 2005+A1:2014, Design of composite steel and concrete structures. General rules. Structural fire design. BSI</ref>. | *BS EN 1994-1-2<ref name="No12">BS EN 1994-1-2: 2005+A1:2014, Design of composite steel and concrete structures. General rules. Structural fire design. BSI</ref>. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
The fire [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Fire_Eurocodes|Eurocodes]] are more comprehensive than [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#BS5950_Part_8|BS5950 Part 8]]<ref name="No9"></ref>. A greater level of detail is available on material properties and, as well as dealing with most of the subjects covered in [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#BS5950_Part_8|BS5950 Part 8]]<ref name="No9"></ref>, the combined suite of fire [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Fire_Eurocodes|Eurocodes]] also introduces the concept of time-temperature relationships for different types of fire, including [[Structural_fire_engineering#Parametric_time-temperature_relationships|parametric fires]]. These are fires which are specific to the conditions in the building being considered. Three levels of calculation are provided: tabular; simple and advanced. | The fire [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Fire_Eurocodes|Eurocodes]] are more comprehensive than [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#BS5950_Part_8|BS5950 Part 8]]<ref name="No9"></ref>. A greater level of detail is available on material properties and, as well as dealing with most of the subjects covered in [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#BS5950_Part_8|BS5950 Part 8]]<ref name="No9"></ref>, the combined suite of fire [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Fire_Eurocodes|Eurocodes]] also introduces the concept of time-temperature relationships for different types of fire, including [[Structural_fire_engineering#Parametric_time-temperature_relationships|parametric fires]]. These are fires which are specific to the conditions in the building being considered. Three levels of calculation are provided: tabular; simple and advanced. | ||
| − | The tabular methods are used for direct design when certain parameters relating to loading, geometry and reinforcement are known. Simple methods are generally considered to be suitable for hand calculation, although they are often quite complex (generally much more so than in [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#BS5950_Part_8|BS5950 Part 8]]<ref name="No9"></ref>) and may often require the development of spreadsheets or bespoke programs. Advanced calculation models are only appropriate for computer analysis and not for general design. | + | The tabular methods are used for direct design when certain parameters relating to loading, geometry and reinforcement are known. Simple methods are generally considered to be suitable for hand calculation, although they are often quite complex (generally much more so than in [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#BS5950_Part_8|BS5950 Part 8]]<ref name="No9"></ref>) and may often require the development of spreadsheets or bespoke programs. Advanced calculation models are only appropriate for computer analysis and not for general design. Free design software is available for the design of both [[#Resources|beams and columns at elevated temperature]]. |
| − | Design [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Fire_Eurocodes|Eurocodes]] are | + | Design [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Fire_Eurocodes|Eurocodes]] are accompanied by National Annexes which provide instruction on values for certain nationally determined parameters and also on elements of the standards which are not applicable in the UK. This recognises the responsibility of the regulatory authorities in each member state to define their own required levels of safety. The National Annex may also contain guidance on the application of informative annexes in the [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Fire_Eurocodes|Eurocodes]] and references to non-contradictory complementary information (NCCI) to assist the user to apply the design rules in the [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Fire_Eurocodes|Eurocodes]]. |
| − | + | ||
| + | Comprehensive advice on the fire resistance of steel framed buildings in accordance with the Eurocodes is given in [[#Resources|SCI P375]], and worked examples following the simplified calculation models, covering the verifications of beams and columns are presented in [[#Resources|SCI-P403]] and available [[#Resources|here]]. | ||
==Fire protecting structural steelwork== | ==Fire protecting structural steelwork== | ||
''Main Articles: [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|Fire protecting structural steelwork]]'' | ''Main Articles: [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|Fire protecting structural steelwork]]'' | ||
| − | Passive fire protection materials insulate steel structures from the effects of the high temperatures that may be generated in fire. They can be divided into two types, non-reactive, of which the most common types are [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Boards|boards]] and [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Sprays|sprays]] and reactive, of which [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|thin film intumescent coatings]] are the best example. [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|Thin film intumescent coatings]] in turn can be either on-site or [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Off_site_applied_intumescent_coatings|off-site applied]]. The UK | + | Passive fire protection materials insulate steel structures from the effects of the high temperatures that may be generated in fire. They can be divided into two types, non-reactive, of which the most common types are [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Boards|boards]] and [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Sprays|sprays]] and reactive, of which [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|thin film intumescent coatings]] are the best example. [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|Thin film intumescent coatings]] in turn can be either on-site or (more commonly) [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Off_site_applied_intumescent_coatings|off-site applied]]. The UK has an efficient and competitive structural fire protection industry which can deliver cost-effective solutions. |
| − | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|Thin film intumescent coatings]] are paint like substances which are inert at low temperatures but which provide insulation by swelling to provide a charred layer of low conductivity material when heated. This char is an excellent insulator. [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|Thin film intumescent coatings]] | + | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|Thin film intumescent coatings]] are paint-like substances which are inert at low temperatures but which provide insulation by swelling to provide a charred layer of low conductivity material when heated. This char is an excellent insulator. [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|Thin film intumescent coatings]] dominate the passive structural [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Trends_in_structural_fire_protection|fire protection market]] in the UK. |
[[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|Thin film intumescent coatings]] can be specified with an aesthetic or a non-aesthetic finish. The cost differential can be considerable and care should be exercised to ensure that the specification is consistent with the visual requirement. | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|Thin film intumescent coatings]] can be specified with an aesthetic or a non-aesthetic finish. The cost differential can be considerable and care should be exercised to ensure that the specification is consistent with the visual requirement. | ||
| Line 77: | Line 81: | ||
[[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Boards|Boards]] are also a popular type of fire protection in the UK. They are widely used both where the protection system is in full view and an aesthetic appearance is required, and where it is hidden. [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Boards|Boards]] can be divided into two families. Those which are suitable for the application of decorative finishes are generally quite heavy, and more expensive, than the non-aesthetic, lighter materials. | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Boards|Boards]] are also a popular type of fire protection in the UK. They are widely used both where the protection system is in full view and an aesthetic appearance is required, and where it is hidden. [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Boards|Boards]] can be divided into two families. Those which are suitable for the application of decorative finishes are generally quite heavy, and more expensive, than the non-aesthetic, lighter materials. | ||
| − | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Sprays|Sprays]] protection systems have decreased in popularity | + | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Sprays|Sprays]] protection systems have decreased in popularity, despite being one of the cheapest forms of fire protection in terms of application costs. This is mainly due to problems with overspray and impacts on the construction program. |
| − | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Flexible_blanket_systems|Flexible, or blanket]], fire protection systems have been developed and fill a niche where complex shapes require protecting but where a dry trade is preferred. | + | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Flexible_blanket_systems|Flexible, or blanket]], fire protection systems have been developed and fill a niche where complex shapes such as truss members require protecting but where a dry trade is preferred. |
| − | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Concrete_encasement|Concrete encasement]] can also be used as fire protection for structural steelwork. | + | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Concrete_encasement|Concrete encasement]] can also be used as fire protection for structural steelwork. This method has only a small percentage of the fire protection market in the UK. [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Block_infilled_columns|Blockwork filling]] between column flanges may be used to increase fire resistance. |
<gallery perrow=3 caption="Fire protection systems" widths=250px heights=250px> | <gallery perrow=3 caption="Fire protection systems" widths=250px heights=250px> | ||
| Line 94: | Line 98: | ||
==Structural fire protection specification== | ==Structural fire protection specification== | ||
{{#image_template:image=File:A_over_V_and_heating_rate.png|caption=[[Calculating_section_factors|Section factor]] and heating rates in fire|align=right|wrap=true|width=300}} | {{#image_template:image=File:A_over_V_and_heating_rate.png|caption=[[Calculating_section_factors|Section factor]] and heating rates in fire|align=right|wrap=true|width=300}} | ||
| − | {{#image_template:image=File: | + | {{#image_template:image=File:ASFP_6th_ed.JPG|caption=The ASFP’s Yellow Book<ref name="No13">Fire protection for structural steel in buildings. Volume 1 6th edition. Association for Specialist Fire Protection</ref>|align=left|wrap=true|width=200}} |
''Main articles: [[Fire protecting structural steelwork| Fire protecting structural steelwork]], [[Calculating section factors| Calculating section factors]]'' | ''Main articles: [[Fire protecting structural steelwork| Fire protecting structural steelwork]], [[Calculating section factors| Calculating section factors]]'' | ||
[[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|Fire protection]] manufacturers’ recommendations for the use and application of their products generally relate the thickness of [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|fire protection]] to the [[Calculating_section_factors|section factor]] and the [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|fire resistance time]] required. The [[Calculating_section_factors|section factor]] is defined as the surface area of the member per unit length (A<sub>m</sub>) divided by the volume per unit length (V). It is measured in units of m<sup>-1</sup>.This was previously calculated as heated perimeter divided by cross sectional area (H<sub>p</sub>/A), which is the same thing for uniform cross-sections. H<sub>p</sub>/A is still occasionally used and perhaps explains the concept more effectively than A<sub>m</sub>/V. | [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|Fire protection]] manufacturers’ recommendations for the use and application of their products generally relate the thickness of [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|fire protection]] to the [[Calculating_section_factors|section factor]] and the [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|fire resistance time]] required. The [[Calculating_section_factors|section factor]] is defined as the surface area of the member per unit length (A<sub>m</sub>) divided by the volume per unit length (V). It is measured in units of m<sup>-1</sup>.This was previously calculated as heated perimeter divided by cross sectional area (H<sub>p</sub>/A), which is the same thing for uniform cross-sections. H<sub>p</sub>/A is still occasionally used and perhaps explains the concept more effectively than A<sub>m</sub>/V. | ||
| − | [[Calculating_section_factors|Section factors]] for a range of common structural and [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|fire protection]] arrangements for [[Steel_construction_products#Standard_open_sections|hot rolled open sections]] can be found in the [[The Blue Book]]. It can also be found in a document published by the [https://asfp. | + | [[Calculating_section_factors|Section factors]] for a range of common structural and [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|fire protection]] arrangements for [[Steel_construction_products#Standard_open_sections|hot rolled open sections]] can be found in the [[The Blue Book]]. It can also be found in a document published by the [https://asfp.org.uk/ Association for Specialist Fire Protection] (ASFP)<ref name="No13"></ref>, (the Yellow Book), which contains, in addition, information on [[Calculating_section_factors|section factors]] for [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|hot finished hollow sections]]. |
The ASFP has extensive guidance for specifiers, fabricators, contractors and enforcement authorities, and anyone else with an interest or responsibility for providing adequate structural fire protection within steel framed buildings. These are issued in the form of Advisory Notes and Technical Guidance Documents. | The ASFP has extensive guidance for specifiers, fabricators, contractors and enforcement authorities, and anyone else with an interest or responsibility for providing adequate structural fire protection within steel framed buildings. These are issued in the form of Advisory Notes and Technical Guidance Documents. | ||
| Line 108: | Line 112: | ||
{{#image_template:image=File:Reinforced_hollow_section_arriving_on_site.jpg |caption=Reinforced hollow section arriving on site |align=right|wrap=true|width=200}} | {{#image_template:image=File:Reinforced_hollow_section_arriving_on_site.jpg |caption=Reinforced hollow section arriving on site |align=right|wrap=true|width=200}} | ||
| − | Hot | + | Hot finished rectangular and circular [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|structural hollow sections]] provide architects and engineers with aesthetically pleasing and robust solutions in structural design. They can achieve a constant external dimension for all weights of a given size, which enables them to achieve standardisation of architectural and structural details throughout the full height of the building. The uniformity of shape and properties means that they more are efficient in certain design conditions than [[Steel_construction_products#Long_products_-_open_sections|open sections]]. |
[[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|Fire resistance]] in [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|structural hollow sections]] can be achieved by the use of external fire protection, usually [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|thin film intumescent coatings ]] or by either [[Hollow_sections_in_fire#Concrete_filled_and_reinforced_structural_hollow_sections|concrete filling with reinforcement]] or by [[Hollow_sections_in_fire#Concrete_filled_hollow_sections_with_external_fire_protection|concrete filling combined with external fire protection]]. By filling [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|hollow sections]] with concrete, a composite section is produced, which will increase the section’s room temperature load carrying capacity, whilst retaining all the advantageous features of the basic unfilled section. Alternatively, for the same original load capacity, it permits smaller composite sections to be used. Any reduction in section size also gives advantages in subsequent construction processes, including a reduced surface area for painting and a reduced footprint (and increased lettable area). | [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|Fire resistance]] in [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|structural hollow sections]] can be achieved by the use of external fire protection, usually [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|thin film intumescent coatings ]] or by either [[Hollow_sections_in_fire#Concrete_filled_and_reinforced_structural_hollow_sections|concrete filling with reinforcement]] or by [[Hollow_sections_in_fire#Concrete_filled_hollow_sections_with_external_fire_protection|concrete filling combined with external fire protection]]. By filling [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|hollow sections]] with concrete, a composite section is produced, which will increase the section’s room temperature load carrying capacity, whilst retaining all the advantageous features of the basic unfilled section. Alternatively, for the same original load capacity, it permits smaller composite sections to be used. Any reduction in section size also gives advantages in subsequent construction processes, including a reduced surface area for painting and a reduced footprint (and increased lettable area). | ||
Filled [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|hollow sections]] will need to contain reinforcement in the mix in order to minimise column dimensions and to sustain the required [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Effect_of_load|fire limit state design loads]] for [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|fire resistance periods]] of 60 minutes or more. | Filled [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|hollow sections]] will need to contain reinforcement in the mix in order to minimise column dimensions and to sustain the required [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Effect_of_load|fire limit state design loads]] for [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|fire resistance periods]] of 60 minutes or more. | ||
| − | [[#Resources|Design guidance]] and [[Design_software_and_tools#FireSoft_-_concrete_filled.2C_hot_finished_structural_hollow_section_columns_in_fire_and_ambient_conditions|software (Firesoft)]] for the design of reinforced, concrete filled [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|hollow sections]] in fire is available. The software is based on the European code for composite construction for ambient condition, EN 1994-1-1<ref name="No14"> BS EN 1994-1-1:2004. Design of composite steel and concrete structures. General rules and rules for buildings BSI</ref>, the main difference between ambient and fire designs being the modifications of mechanical properties at elevated temperatures for the fire conditions. | + | [[#Resources|Design guidance (SCI P259)]] and [[Design_software_and_tools#FireSoft_-_concrete_filled.2C_hot_finished_structural_hollow_section_columns_in_fire_and_ambient_conditions|software (Firesoft)]] for the design of reinforced, concrete filled [[Steel_construction_products#Structural_hollow_sections|hollow sections]] in fire is available. The software is based on the European code for composite construction for ambient condition, EN 1994-1-1<ref name="No14"> BS EN 1994-1-1:2004. Design of composite steel and concrete structures. General rules and rules for buildings BSI</ref>, the main difference between ambient and fire designs being the modifications of mechanical properties at elevated temperatures for the fire conditions. |
==Composite steel deck floors in fire== | ==Composite steel deck floors in fire== | ||
| Line 123: | Line 127: | ||
[[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire#Assessment_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_with_mesh_reinforcement|Mesh]] reinforcement can be that present in ordinary room temperature design; it may not be necessary to add more solely for the fire condition. It is not normally necessary to fire protect the exposed soffit of the steel deck. | [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire#Assessment_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_with_mesh_reinforcement|Mesh]] reinforcement can be that present in ordinary room temperature design; it may not be necessary to add more solely for the fire condition. It is not normally necessary to fire protect the exposed soffit of the steel deck. | ||
| − | Two methods are available for the design of [[Floor_systems#Composite_slabs|composite steel deck floors]] designed to BS 5950 Part 4<ref name="No15">BS 5950-4: 1994, Structural use of steelwork in building. Code of practice for design of composite slabs with profiled steel sheeting, BSI</ref> for fire when using mesh reinforcement. Both are described in the SCI publication, [[#Resources|P056]]. These are the [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire# Assessment_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_with_mesh_reinforcement|fire engineering]] and the [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire# Assessment_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_with_mesh_reinforcement|simplified]] method. Most decking manufacturers provide extensive data on slab details for given periods of [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|fire resistance]]. These are usually based on the [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire# Assessment_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_with_mesh_reinforcement|simplified]] method although the [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire#Assessment_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_with_mesh_reinforcement|fire engineering]] method is occasionally used (usually signified by the presence of bottom reinforcing bars in the slab). | + | Two methods are available for the design of [[Floor_systems#Composite_slabs|composite steel deck floors]] designed to BS 5950 Part 4<ref name="No15">BS 5950-4: 1994, Structural use of steelwork in building. Code of practice for design of composite slabs with profiled steel sheeting, BSI</ref> for fire when using mesh reinforcement. Both are described in the SCI publication, [[#Resources|P056]]. These are the [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire# Assessment_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_with_mesh_reinforcement|fire engineering]] and the [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire# Assessment_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_with_mesh_reinforcement|simplified]] method. Most decking manufacturers provide extensive data on slab details for given periods of [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|fire resistance]] allowing the designer to simply select a solution from a table. These are usually based on the [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire# Assessment_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_with_mesh_reinforcement|simplified]] method although the [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire#Assessment_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_with_mesh_reinforcement|fire engineering]] method is occasionally used (usually signified by the presence of bottom reinforcing bars in the slab). |
BS EN 1994-1-2<ref name="No12"></ref> also contains a simplified method for calculating the design moment of resistance of [[Floor_systems#Composite_slabs|composite steel deck floor]] slabs with mesh reinforcement. It should be noted that Annex D, ''Model for the calculation of the fire resistance of unprotected composite slabs exposed to fire beneath the slab according to the standard temperature-time curve'' is not applicable in the UK. | BS EN 1994-1-2<ref name="No12"></ref> also contains a simplified method for calculating the design moment of resistance of [[Floor_systems#Composite_slabs|composite steel deck floor]] slabs with mesh reinforcement. It should be noted that Annex D, ''Model for the calculation of the fire resistance of unprotected composite slabs exposed to fire beneath the slab according to the standard temperature-time curve'' is not applicable in the UK. | ||
| − | Research has shown that [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire#Filling_of_voids|filling the voids]] between the raised parts of the deck profile and the top flange of a [[Composite_construction#Downstand_beams|downstand beam]] in [[Composite_construction|composite construction]] is not always necessary. The upper flange of a [[Composite_construction#Types_of_composite_beam|composite beam]] is so close to the plastic neutral axis that it makes little contribution to the bending strength of the member as a whole. Thus, the temperature of the upper flange can often be allowed to increase, with a corresponding [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Steelwork_strength_in_fire|decrease in its strength]], without significantly adversely affecting the capacity of the composite system. Details of when to [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire#Filling_of_voids|fill the voids]] are widely available. They are given in [[#Resources|SCI | + | Research has shown that [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire#Filling_of_voids|filling the voids]] between the raised parts of the deck profile and the top flange of a [[Composite_construction#Downstand_beams|downstand beam]] in [[Composite_construction|composite construction]] is not always necessary. The upper flange of a [[Composite_construction#Types_of_composite_beam|composite beam]] is so close to the plastic neutral axis that it makes little contribution to the bending strength of the member as a whole. Thus, the temperature of the upper flange can often be allowed to increase, with a corresponding [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Steelwork_strength_in_fire|decrease in its strength]], without significantly adversely affecting the capacity of the composite system. Details of when to [[Design_of_composite_steel_deck_floors_for_fire#Filling_of_voids|fill the voids]] are widely available. They are given in [[#Resources|SCI P359]] and also in the Yellow Book<ref name="No13"></ref>. |
==External steelwork in fire== | ==External steelwork in fire== | ||
| Line 134: | Line 138: | ||
Modern steel framed buildings are sometimes constructed with the structural frame on the outside of the facade. Since, in the event of a fire, an external structural frame will be heated only by flames emanating from windows or other openings in the building facade, the fire that the external steelwork experiences may be less severe than that to which the steel inside the building is exposed. | Modern steel framed buildings are sometimes constructed with the structural frame on the outside of the facade. Since, in the event of a fire, an external structural frame will be heated only by flames emanating from windows or other openings in the building facade, the fire that the external steelwork experiences may be less severe than that to which the steel inside the building is exposed. | ||
| − | It may be possible to design the frame members to remain unprotected or to have reduced protection if they are positioned so that they will not be engulfed by flames and hot gases issuing from facade openings. Assessment can be carried out in accordance with [[#Resources|SCI | + | It may be possible to design the frame members to remain unprotected or to have reduced protection if they are positioned so that they will not be engulfed by flames and hot gases issuing from facade openings. Assessment can be carried out in accordance with [[#Resources|SCI P375]]. This describes the calculation process involved in determining the temperatures reached by external steel subject to a fire in an adjacent compartment. It involves calculation of: the flame velocity; the flame height above the window; the horizontal flame projection; the effective flame temperature; the flame emissivity; the configuration factor for the flame with respect to the steel the effective fire temperature; the configuration factor for the openings with respect to the steel; and the rate of burning within the compartment. |
BS EN 1993-1-2<ref name="No11"></ref> Appendix B also contains a method for calculation of the size and temperature of flames from openings and radiation and convection parameters for heat transfer calculations. | BS EN 1993-1-2<ref name="No11"></ref> Appendix B also contains a method for calculation of the size and temperature of flames from openings and radiation and convection parameters for heat transfer calculations. | ||
| − | Where external steel is not required to be aesthetic and/or it requires resistance to damage and abrasion, [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Concrete_encasement|concrete encasement]] is still sometimes used as a form of fire protection. Some [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Sprays|spray protection]] materials can also be used and | + | Where external steel is not required to be aesthetic and/or it requires resistance to damage and abrasion, [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Concrete_encasement|concrete encasement]] is still sometimes used as a form of fire protection. Some [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Sprays|spray protection]] materials can also be used and may also be suitable for situations where the risk is from [[Fire_testing#Other_standard_fire_tests|hydrocarbon fires]]. |
| − | The most common form of fire protection used on external steel is [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|thin film intumescent | + | The most common form of fire protection used on external steel is [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thin_film_intumescent_coatings|thin film intumescent coating]]. It should be recognised that there will be a limit on the time for which the manufacturers will guarantee the performance of their materials. Care should always be taken to ensure that the manufacturers’ application specification is followed so that the performance guarantee is valid. |
In addition, [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thick_film_intumescent_coatings|thick film epoxy intumescents]] are used to fire protect external steel. A case study is available [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Case_studies|here]]. These are also available as precast products. | In addition, [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Thick_film_intumescent_coatings|thick film epoxy intumescents]] are used to fire protect external steel. A case study is available [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork#Case_studies|here]]. These are also available as precast products. | ||
| Line 150: | Line 154: | ||
''Main articles: [[Car_parks_in_fire|Car parks in fire]], [[Calculating_section_factors|Calculating section factors]]'' | ''Main articles: [[Car_parks_in_fire|Car parks in fire]], [[Calculating_section_factors|Calculating section factors]]'' | ||
| − | For the purposes of fire | + | For the purposes of fire resistance, car parks for light vehicles can be classed as either open sided, or all other types. [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> defines the requirements for open sided car parks. [[Car_parks_in_fire#Open_car_parks|Open car parks]] can be considered as a special case of [[Fire_and_steel_construction#External_steelwork_in_fire|external steelwork]]. In the UK, the authorities recognise that there is a low risk of fire spread and ample opportunity for smoke and hot gases to be dissipated in [[Car_parks_in_fire#Open_car_parks|open car parks]] when [[Car_parks_in_fire#Open_car_parks|certain ventilation criteria]] are met. Therefore [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|fire resistance requirements]] are low and the steel frame is generally unprotected as long as defined [[Calculating_section_factors|section factor]] requirements are also met. |
The [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|fire resistance requirements]] for other car parks are typically consistent with those for commercial buildings of the same height. | The [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|fire resistance requirements]] for other car parks are typically consistent with those for commercial buildings of the same height. | ||
| Line 160: | Line 164: | ||
In the UK, structural frames in [[Single_storey_industrial_buildings|single storey buildings]] do not normally require fire protection. [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref>, Section 7.3, excludes from the definition of elements of structure, that structure which only supports a roof. This is because the provisions of the Building Regulations exist mainly for the purposes of life safety and fires in [[Single_storey_industrial_buildings|single storey buildings]] are not generally considered to pose a significant threat in that regard. | In the UK, structural frames in [[Single_storey_industrial_buildings|single storey buildings]] do not normally require fire protection. [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref>, Section 7.3, excludes from the definition of elements of structure, that structure which only supports a roof. This is because the provisions of the Building Regulations exist mainly for the purposes of life safety and fires in [[Single_storey_industrial_buildings|single storey buildings]] are not generally considered to pose a significant threat in that regard. | ||
| − | + | Fire resistance is required when [[Single_storey_industrial_buildings|single storey non-domestic buildings]] are located close to a boundary. The objective is to stop fire spreading to adjacent buildings. The Building Regulations define when a building falls within the scope of a [[Single_storey_buildings_in_fire_boundary_conditions#Boundary_conditions_defined|boundary condition]] | |
| − | Where a [[Single_storey_industrial_buildings|single storey building]] exists in a [[Single_storey_buildings_in_fire_boundary_conditions#Boundary_conditions_defined|boundary condition]], it has been widely accepted that it is necessary only for the affected | + | Where a [[Single_storey_industrial_buildings|single storey building]] exists in a [[Single_storey_buildings_in_fire_boundary_conditions#Boundary_conditions_defined|boundary condition]], it has been widely accepted that it is necessary only for the affected elevation and its supporting steel columns to be [[Fire_protecting_structural_steelwork|fire protected]]. The rafters may be left unprotected but the column base must be designed to resist the overturning moment caused by the collapse of the unprotected parts of the building in fire. The method of calculation used to derive the horizontal forces and moments created by rafter collapse is given in [[#Resources|SCI P313]]; this is referenced in Section 13.15 of [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> and Section 2.D.2 of [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Technical_Handbook_2022|Scottish Technical Handbook 2022]]<ref name="No3"></ref>. |
==Active fire protection== | ==Active fire protection== | ||
| Line 168: | Line 172: | ||
''Main articles: [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes|Sprinklers in UK fire codes]]'' | ''Main articles: [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes|Sprinklers in UK fire codes]]'' | ||
| − | Sprinklers are designed to suppress automatically small fires on, or shortly after, ignition or to contain fires until the arrival of the fire service. In England [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes# | + | Sprinklers are designed to suppress automatically small fires on, or shortly after, ignition or to contain fires until the arrival of the fire service. In England [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes#Concessions_in_Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> requires that almost all buildings over 30 metres in height are required to have an approved life safety sprinkler system installed. A reduction of 30 minutes in the required [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|fire resistance]] may be applied to many types of occupancies less than 30 metres in height when a life safety sprinkler system is installed and other concessions are also possible. [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes#Concessions_in_Technical_Booklet_E|Technical Booklet E]]<ref name="No4"></ref> addresses the issue in a similar way. |
| − | In the special case of large shopping complexes, [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes# | + | In the special case of large shopping complexes, [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes#Concessions_in_Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> requires that the provisions of BS 9999<ref name="No5></ref> are followed for fire precautions and this usually means that a life safety sprinkler system is installed for any covered shopping complex. |
| − | In [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes# | + | In [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes#Concessions_in_Technical_Handbook_2022|Scottish Technical Handbook 2022]]<ref name="No3"></ref>, sprinklers are not mandatory in most buildings, with the following exceptions: enclosed [[Retail_buildings|shopping centres]]; residential care buildings; sheltered housing complexes, [[Education_buildings|school]] buildings ; a building containing flats or maisonettes; social housing and shared multi-occupancy residential buildings. |
| − | [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes# | + | |
| + | [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes#Concessions_in_BS_9999|BS 9999]]<ref name="No5"></ref> also allows concessions for sprinklers. In general, these are more attractive than those on offer in [[Sprinklers_in_UK_fire_codes#Concessions_in_Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> and can affect issues such as [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements|structural fire resistance]], maximum travel distances and minimum door widths. | ||
==Structural fire engineering== | ==Structural fire engineering== | ||
| Line 179: | Line 184: | ||
''Main articles: [[Structural_fire_engineering|Structural fire engineering]]'' | ''Main articles: [[Structural_fire_engineering|Structural fire engineering]]'' | ||
| − | Increasing innovation in design, construction and usage of modern buildings has created a situation where it is sometimes difficult to satisfy the functional requirements of the [[Fire_and_steel_construction#The_Building_Regulations_and_fire_precautions_in_buildings|Building Regulations]] by the use only of the provisions given in [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref>, [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements# | + | Increasing innovation in design, construction and usage of modern buildings has created a situation where it is sometimes difficult to satisfy the functional requirements of the [[Fire_and_steel_construction#The_Building_Regulations_and_fire_precautions_in_buildings|Building Regulations]] by the use only of the provisions given in [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref>, [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Technical_Handbook_2022|Scottish Technical Handbook 2022]] <ref name="No3"></ref> and [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Technical_Booklet_E|Technical Booklet E]]<ref name="No4"></ref>. Recognition of this, and also increased knowledge of how real buildings react in fire and of how real fires behave, has led many authorities to acknowledge that improvements in fire safety may now be possible in many instances by adopting a comprehensive analytical and engineering approach to the particular structure and risks. This has been supported by a wide ranging and intensive programme of research and development world-wide. Thus [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> states that: |
''Fire safety engineering can provide an alternative approach to fire safety. It may be the only practical way to achieve a satisfactory standard of safety in some large and complex buildings and in buildings containing different uses.'' | ''Fire safety engineering can provide an alternative approach to fire safety. It may be the only practical way to achieve a satisfactory standard of safety in some large and complex buildings and in buildings containing different uses.'' | ||
[[Structural_fire_engineering|Fire safety engineering]] can be seen as an integrated package of measures designed to achieve the maximum benefit from the available methods of preventing, controlling or limiting the consequences of fire. The Institution of Structural Engineers says of structural fire engineering: ''By adopting a performance based approach to structural fire engineering….more economic designs can be achieved and more innovative and complex buildings can be constructed''<ref name="No17"></ref>. | [[Structural_fire_engineering|Fire safety engineering]] can be seen as an integrated package of measures designed to achieve the maximum benefit from the available methods of preventing, controlling or limiting the consequences of fire. The Institution of Structural Engineers says of structural fire engineering: ''By adopting a performance based approach to structural fire engineering….more economic designs can be achieved and more innovative and complex buildings can be constructed''<ref name="No17"></ref>. | ||
| − | The move from prescriptive to functional requirements in the [[Fire_and_steel_construction#The_Building_Regulations_and_fire_precautions_in_buildings|Building Regulations]] in the United Kingdom provided a huge boost to the development of [[Structural_fire_engineering|fire engineering]] | + | The move from prescriptive to functional requirements in the [[Fire_and_steel_construction#The_Building_Regulations_and_fire_precautions_in_buildings|Building Regulations]] in the United Kingdom provided a huge boost to the development of [[Structural_fire_engineering|fire engineering]]. As a consequence, the majority of tall and complex buildings now benefit from an engineered approach to fire rather than relying on the prescriptive provisions of [[Structural_fire_resistance_requirements#Approved_Document_B|Approved Document B]]<ref name="No2"></ref> or similar. This has proved beneficial to the construction industry as a whole, but particularly to the steel construction sector, which has carried out most of the research and whose structures consequently offer the greatest potential for improved solutions using [[Structural_fire_engineering|fire engineering]]. |
| + | |||
| + | An example of [[Structural_fire_engineering|fire engineering]] is the consideration of localised fires rather than assuming that the temperature of an entire compartment within a building rises uniformly. Undertaking a performance-based fire engineering approach for certain types of structures such as airports and other large open buildings will produce a more accurate and more economic [[Design|design]]. The analysis involves an assessment of the material that may cause the fire, the size and ventilation characteristics of the compartment and is considerably more complex than following a prescriptive approach. Guidance on the effect of localised fires on columns is given in [[#Resources|SCI P423]]. | ||
==Structural steel after fire== | ==Structural steel after fire== | ||
| Line 191: | Line 198: | ||
''Main Articles: [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards|Design using structural fire standards]], [[Fire_damage_assessment_of_hot_rolled_structural_steelwork|Fire damage assessment of hot rolled structural steelwork]]'' | ''Main Articles: [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards|Design using structural fire standards]], [[Fire_damage_assessment_of_hot_rolled_structural_steelwork|Fire damage assessment of hot rolled structural steelwork]]'' | ||
| − | Fire will affect structural steel and the extent of the impact needs to assessed once the fire has been extinguished. On many occasions fire | + | Fire will affect structural steel and the extent of the impact needs to assessed once the fire has been extinguished. On many occasions steelwork exposed to fire shows little or no distortion, and this leads to uncertainty as to how it has been affected. This is particularly true in situations where fire has resulted in some parts of the structure exhibiting little or no damage alongside areas where considerable damage and distortion are clearly visible. |
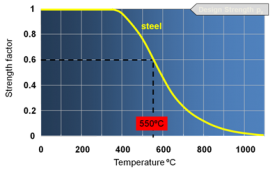
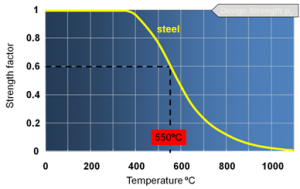
| − | All materials weaken with increasing temperature and steel is no exception. [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Steelwork_strength_in_fire|Strength loss for steel]] is generally accepted to begin at about 300°C and increases rapidly after 400°C. By 550°C the most common grades | + | All materials weaken with increasing temperature and steel is no exception. [[Design_using_structural_fire_standards#Steelwork_strength_in_fire|Strength loss for steel]] is generally accepted to begin at about 300°C and increases rapidly after 400°C. By 550°C the most common grades of [[Steel_construction_products#Standard_open_sections|hot rolled structural steel]] retain about 60% of their room temperature yield strength. This is often considered to be the failure temperature for structural steel, but in practice this is a very conservative assumption - the calculated failure temperature may be significantly higher. |
| − | Structural steels that are heated above 600°C will lose some of their properties on cooling. The extent of this loss is a function of the grade of steel, with the | + | Structural steels that are heated above 600°C will lose some of their properties on cooling. The extent of this loss is a function of the grade of steel, with the higher grades being most affected. Tests exist to check if any such loss of properties has taken place. |
Fires can also cause distortion and yielding in [[Fire_damage_assessment_of_hot_rolled_structural_steelwork#Connections_and_foundations|bolts and connections]] due to thermal expansion and contraction. Checks should always be carried out to determine if this has led to weld cracking, bolt shearing etc. | Fires can also cause distortion and yielding in [[Fire_damage_assessment_of_hot_rolled_structural_steelwork#Connections_and_foundations|bolts and connections]] due to thermal expansion and contraction. Checks should always be carried out to determine if this has led to weld cracking, bolt shearing etc. | ||
| Line 212: | Line 219: | ||
==Resources== | ==Resources== | ||
| + | *[[Media:Steel_Construction_Fire_Protection_2024.pdf|Steel Construction - Fire Protection Supplement, 2024]] | ||
*[[Media:Steel_construction_-_Fire_Protection.pdf|Steel construction - Fire Protection supplement, 2013]] | *[[Media:Steel_construction_-_Fire_Protection.pdf|Steel construction - Fire Protection supplement, 2013]] | ||
*[[Media:SCI_P56.pdf|SCI P056 The Fire Resistance of Composite Floors with Steel Decking, 2nd ed.]] | *[[Media:SCI_P56.pdf|SCI P056 The Fire Resistance of Composite Floors with Steel Decking, 2nd ed.]] | ||
| Line 218: | Line 226: | ||
*[[Media:SCI_P124.pdf|SCI P124. The fire resistance of web-infilled steel columns, 1992]] | *[[Media:SCI_P124.pdf|SCI P124. The fire resistance of web-infilled steel columns, 1992]] | ||
*[[Media:SCI_P126.pdf|SCI P126 The fire resistance of shelf angle floor beams to BS5950 Part 8, 1993]] | *[[Media:SCI_P126.pdf|SCI P126 The fire resistance of shelf angle floor beams to BS5950 Part 8, 1993]] | ||
| + | *[https://portal.steel-sci.com/documents.html SCI P186 Design of Steel Framed Buildings without Applied Fire Protection, 1999] | ||
| + | *[https://portal.steel-sci.com/documents.html SCI P259 The Fire Resistance of Concrete Filled Tubes to Eurocode 4, 2000] | ||
*[[Media:SCI_P313.pdf|SCI P313, Single Storey Steel Framed Buildings in Fire Boundary Conditions]] | *[[Media:SCI_P313.pdf|SCI P313, Single Storey Steel Framed Buildings in Fire Boundary Conditions]] | ||
| + | *[[Media:SCI_P359.pdf|SCI P359 Composite Design of Steel Framed Buildings, 2011]] | ||
*[[media:SCI_P363.pdf|SCI P363 Steel Building Design: Design Data, 2013]]<br>A web-based interactive version of the '[[Design_software_and_tools#Interactive_.22Blue_Book.22|Blue Book]]', is also available. | *[[media:SCI_P363.pdf|SCI P363 Steel Building Design: Design Data, 2013]]<br>A web-based interactive version of the '[[Design_software_and_tools#Interactive_.22Blue_Book.22|Blue Book]]', is also available. | ||
*[[Media:SCI_P375.pdf|SCI P375 Fire Resistance Design of Steel Framed Buildings]] | *[[Media:SCI_P375.pdf|SCI P375 Fire Resistance Design of Steel Framed Buildings]] | ||
| − | *[https://portal.steel-sci.com/ | + | *[https://portal.steel-sci.com/documents.html SCI P403 Resistance of beams & columns in fire: Worked examples to the Eurocodes, 2014] |
| + | *[https://research.bauforumstahl.de/fileadmin/user_upload/LOCAFIplus_Design_Guide_UK.pdf SCI P423 Design of columns subject to localised fires, 2018] | ||
| + | *[https://portal.steel-sci.com/documents.html SCI P424 Fire resistance of Light Steel Framing, 2021] | ||
| + | *[https://portal.steel-sci.com/documents.html SCI P429 Fire Resistance to Steel Sections Galvanized to EN ISO 1461, 2020] | ||
*[http://www.mace.manchester.ac.uk/project/research/structures/strucfire/DataBase/References/Reinstatement_Fire_Damaged_Steel.pdf The Reinstatement of Fire Damaged Iron and Steel Framed Structures] | *[http://www.mace.manchester.ac.uk/project/research/structures/strucfire/DataBase/References/Reinstatement_Fire_Damaged_Steel.pdf The Reinstatement of Fire Damaged Iron and Steel Framed Structures] | ||
*[[Media:CFT_Design_Guide_March_2014.pdf|NCCI: PN006a-GB Design of reinforced, concrete filled, hot finished structural steel hollow sections in fire]] | *[[Media:CFT_Design_Guide_March_2014.pdf|NCCI: PN006a-GB Design of reinforced, concrete filled, hot finished structural steel hollow sections in fire]] | ||
| Line 248: | Line 262: | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | *[https://asfp. | + | *[https://asfp.org.uk/ Association for Specialist Fire Protection] |
== CPD == | == CPD == | ||
Latest revision as of 12:59, 1 April 2025
Structural performance in the fire condition is an important design consideration for all materials. The strength of steel reduces at elevated temperatures, so structural steelwork will generally need protection if the resistance of an unprotected member cannot be justified. Fire protection materials have been developed over many years to provide an effective solution. In parallel, much research has been undertaken into the performance of members and buildings at elevated temperatures, leading to comprehensive design rules such as BS 5950-8[1] and BS EN 1993-1-2[2]
A 2024 update on the fire performance and fire protection of structural steelwork gives a high-level overview for clients and their design teams. This summary makes particular reference to the Regulatory changes being introduced under the 2022 Building Safety Act.
- Structural fire engineering case studies
[top]The Building Regulations and fire precautions in buildings
Main articles: Structural fire resistance requirements
The obligations placed on those who design and construct buildings to ensure that they are both safe and healthy are contained in the Building Regulations. The requirements of the regulations are set out in functional terms, i.e. they outline what must be achieved, but do not prescribe how the requirements are to be satisfied.
For example, Requirement B3(1) of the Building Regulations for England states that The building shall be designed and constructed so that, in the event of a fire, its stability will be maintained for a reasonable period. The equivalent requirement (2.3) in the Scottish Building Regulations states that Every building must be designed and constructed in such a way that in the event of an outbreak of fire within the building, the load-bearing capacity of the building will continue to function until all occupants have escaped, or been assisted to escape, from the building and any fire containment measures have been initiated.
The Governments of the various regions of the UK publish documents which provide guidance on means by which compliance can be achieved. In terms of fire, the most widely used of these is England's Approved Document B[3]. Amongst the various rules for fire safety in buildings contained in this document are details of the structural fire resistance requirements to meet the obligations for structural stability described above. For example, an office building over 30 metres in height requires 120 minutes fire resistance plus a life safety sprinkler system. An assembly building between 18 and 30 metres in height requires 90 minutes fire resistance, unless it has a sprinkler system when the fire resistance period reduces to 60 minutes. Until April 2014, this document was shared between England & Wales but in that month, a separate document was issued for Wales[4]. The differences between these are small but it is necessary to know that they exist.
Welsh Approved Document B[4]
In Scotland the equivalent document is Scottish Technical Handbook 2022[5] and in Northern Ireland it is Technical Booklet E[6]. Some local and building specific regulations are also in place.
All the Government documents provide provision for alternative solutions using fire safety engineering approaches. Approved Document B[3] paragraph 0.18 states that Fire safety engineering might provide an alternative approach to fire safety. Fire safety engineering may be the only practical way to achieve a satisfactory standard of fire safety in some complex buildings and buildings that contain different uses.
In recent years, as the result of extensive research into the nature of fire, how it spreads and the risk factors in building fires, the British Standards Institute has published BS 9999[7]. The intention behind the development of the document is to provide a more transparent and flexible approach to fire safe design through the use of a structured approach to risk.
[top]Steelwork fire resistance
Main articles: Fire testing, Design using structural fire standards
All structural steel sections have some inherent fire resistance and this is a function of the size of the section, its degree of exposure to the fire and the load that it carries.
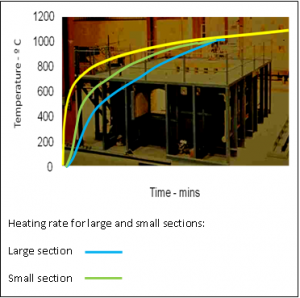
The fire resistance of an element is usually defined as the time for which the element can satisfy appropriate criteria (for example, its load-carrying resistance). Tests are undertaken in a furnace where the temperature follows a standard time-temperature relationship as shown, which is the same for all materials. The standard time-temperature curve does not follow the general behaviour in a real fire, where the temperature falls once the fire load (matter which burns) has been consumed. The fire resistance periods obtained in a test are a measure of the adequacy of the construction in a fire but have no direct relationship with the duration of a real fire. BS 476-20[8], ISO 834[9] and BS EN 1363-1[10] describe the standard test.
The strength of structural steel decreases with temperature. Following an extensive series of standard fire tests, that strength reduction has been quantified. Recent international research has also shown that the limiting (failure) temperature of a structural steel member is not fixed but varies according to two factors, the temperature profile through the cross section and the design load.
For small, fully loaded sections, exposed on all four sides, the inherent fire resistance without added protection can be as little as 12 minutes. For very large sections, lightly loaded and with some partial protection from concrete floor slabs on the upper flange, this can be as high as 50 minutes. Where the heated perimeter is further reduced by the method of the construction (e.g. shallow floor systems), up to 60 minutes inherent fire resistance can be achieved. SCI-P186 describes methods of designing steel framed buildings for 30 and 60 minutes fire resistance without applied fire protection.
The standard fire test time-temperature relationship
Where the inherent fire resistance of the steel is less than that necessary to meet the requirements for structural stability for the building, additional precautions must be taken. This usually takes the form of applied fire protection which insulates the steel from the increasing temperatures. The fire resistance of hollow sections may be increased by concrete filling, which may mean that external fire protection is not required.
[top]Design using structural fire standards
Main articles: Fire testing, Design using structural fire standards,Structural fire engineering
The world’s first design code for steel in fire, BS 5950 Part 8[1] was published in the UK in 1990 and redrafted in 2003. It is based on extensive testing by Tata Steel and the Building Research Establishment (BRE) and brings together in one document details of many of the methods of achieving fire resistance for structural steelwork. Although it is based on evaluation of performance of structural steel members in the standard fire test, it may also be used in fire engineering assessments when parametric fire temperatures are derived by calculation.
BS5950 Part 8[1] also includes design information and guidance for design of portal frames, hollow sections in fire, external steelwork, composite slabs and calculation of fire protection thicknesses based on limiting (failure) temperatures. Background to the standard and worked examples (to the 1990 version) are given in SCI P080.
The following Eurocodes describe the rules for the fire design of buildings using structural steelwork:
The fire Eurocodes are more comprehensive than BS5950 Part 8[1]. A greater level of detail is available on material properties and, as well as dealing with most of the subjects covered in BS5950 Part 8[1], the combined suite of fire Eurocodes also introduces the concept of time-temperature relationships for different types of fire, including parametric fires. These are fires which are specific to the conditions in the building being considered. Three levels of calculation are provided: tabular; simple and advanced.
The tabular methods are used for direct design when certain parameters relating to loading, geometry and reinforcement are known. Simple methods are generally considered to be suitable for hand calculation, although they are often quite complex (generally much more so than in BS5950 Part 8[1]) and may often require the development of spreadsheets or bespoke programs. Advanced calculation models are only appropriate for computer analysis and not for general design. Free design software is available for the design of both beams and columns at elevated temperature.
Design Eurocodes are accompanied by National Annexes which provide instruction on values for certain nationally determined parameters and also on elements of the standards which are not applicable in the UK. This recognises the responsibility of the regulatory authorities in each member state to define their own required levels of safety. The National Annex may also contain guidance on the application of informative annexes in the Eurocodes and references to non-contradictory complementary information (NCCI) to assist the user to apply the design rules in the Eurocodes.
Comprehensive advice on the fire resistance of steel framed buildings in accordance with the Eurocodes is given in SCI P375, and worked examples following the simplified calculation models, covering the verifications of beams and columns are presented in SCI-P403 and available here.
[top]Fire protecting structural steelwork
Main Articles: Fire protecting structural steelwork
Passive fire protection materials insulate steel structures from the effects of the high temperatures that may be generated in fire. They can be divided into two types, non-reactive, of which the most common types are boards and sprays and reactive, of which thin film intumescent coatings are the best example. Thin film intumescent coatings in turn can be either on-site or (more commonly) off-site applied. The UK has an efficient and competitive structural fire protection industry which can deliver cost-effective solutions.
Thin film intumescent coatings are paint-like substances which are inert at low temperatures but which provide insulation by swelling to provide a charred layer of low conductivity material when heated. This char is an excellent insulator. Thin film intumescent coatings dominate the passive structural fire protection market in the UK.
Thin film intumescent coatings can be specified with an aesthetic or a non-aesthetic finish. The cost differential can be considerable and care should be exercised to ensure that the specification is consistent with the visual requirement.
Boards are also a popular type of fire protection in the UK. They are widely used both where the protection system is in full view and an aesthetic appearance is required, and where it is hidden. Boards can be divided into two families. Those which are suitable for the application of decorative finishes are generally quite heavy, and more expensive, than the non-aesthetic, lighter materials.
Sprays protection systems have decreased in popularity, despite being one of the cheapest forms of fire protection in terms of application costs. This is mainly due to problems with overspray and impacts on the construction program.
Flexible, or blanket, fire protection systems have been developed and fill a niche where complex shapes such as truss members require protecting but where a dry trade is preferred.
Concrete encasement can also be used as fire protection for structural steelwork. This method has only a small percentage of the fire protection market in the UK. Blockwork filling between column flanges may be used to increase fire resistance.
- Fire protection systems
Aesthetic thin film intumescent coating.
(Image courtesy of Sherwin-Williams Protective and Marine Coatings)Spray protection.
(Image courtesy of Promat Ltd.)Flexible blanket
(Image courtesy of Thermal Ceramics Ltd.)
[top]Structural fire protection specification
Main articles: Fire protecting structural steelwork, Calculating section factors
Fire protection manufacturers’ recommendations for the use and application of their products generally relate the thickness of fire protection to the section factor and the fire resistance time required. The section factor is defined as the surface area of the member per unit length (Am) divided by the volume per unit length (V). It is measured in units of m-1.This was previously calculated as heated perimeter divided by cross sectional area (Hp/A), which is the same thing for uniform cross-sections. Hp/A is still occasionally used and perhaps explains the concept more effectively than Am/V.
Section factors for a range of common structural and fire protection arrangements for hot rolled open sections can be found in the The Blue Book. It can also be found in a document published by the Association for Specialist Fire Protection (ASFP)[13], (the Yellow Book), which contains, in addition, information on section factors for hot finished hollow sections.
The ASFP has extensive guidance for specifiers, fabricators, contractors and enforcement authorities, and anyone else with an interest or responsibility for providing adequate structural fire protection within steel framed buildings. These are issued in the form of Advisory Notes and Technical Guidance Documents.
[top]Hollow sections in fire
Main articles: Hollow sections in fire
Hot finished rectangular and circular structural hollow sections provide architects and engineers with aesthetically pleasing and robust solutions in structural design. They can achieve a constant external dimension for all weights of a given size, which enables them to achieve standardisation of architectural and structural details throughout the full height of the building. The uniformity of shape and properties means that they more are efficient in certain design conditions than open sections.
Fire resistance in structural hollow sections can be achieved by the use of external fire protection, usually thin film intumescent coatings or by either concrete filling with reinforcement or by concrete filling combined with external fire protection. By filling hollow sections with concrete, a composite section is produced, which will increase the section’s room temperature load carrying capacity, whilst retaining all the advantageous features of the basic unfilled section. Alternatively, for the same original load capacity, it permits smaller composite sections to be used. Any reduction in section size also gives advantages in subsequent construction processes, including a reduced surface area for painting and a reduced footprint (and increased lettable area). Filled hollow sections will need to contain reinforcement in the mix in order to minimise column dimensions and to sustain the required fire limit state design loads for fire resistance periods of 60 minutes or more.
Design guidance (SCI P259) and software (Firesoft) for the design of reinforced, concrete filled hollow sections in fire is available. The software is based on the European code for composite construction for ambient condition, EN 1994-1-1[14], the main difference between ambient and fire designs being the modifications of mechanical properties at elevated temperatures for the fire conditions.
[top]Composite steel deck floors in fire
Main articles: Composite steel deck floors in fire, Fire protecting structural steelwork
A composite steel deck floor is designed in bending as either a series of simply supported spans or a continuous slab. The strength of the floor in fire is provided by the inclusion of mesh (fabric) or fibre reinforcement.
Mesh reinforcement can be that present in ordinary room temperature design; it may not be necessary to add more solely for the fire condition. It is not normally necessary to fire protect the exposed soffit of the steel deck.
Two methods are available for the design of composite steel deck floors designed to BS 5950 Part 4[15] for fire when using mesh reinforcement. Both are described in the SCI publication, P056. These are the fire engineering and the simplified method. Most decking manufacturers provide extensive data on slab details for given periods of fire resistance allowing the designer to simply select a solution from a table. These are usually based on the simplified method although the fire engineering method is occasionally used (usually signified by the presence of bottom reinforcing bars in the slab). BS EN 1994-1-2[12] also contains a simplified method for calculating the design moment of resistance of composite steel deck floor slabs with mesh reinforcement. It should be noted that Annex D, Model for the calculation of the fire resistance of unprotected composite slabs exposed to fire beneath the slab according to the standard temperature-time curve is not applicable in the UK.
Research has shown that filling the voids between the raised parts of the deck profile and the top flange of a downstand beam in composite construction is not always necessary. The upper flange of a composite beam is so close to the plastic neutral axis that it makes little contribution to the bending strength of the member as a whole. Thus, the temperature of the upper flange can often be allowed to increase, with a corresponding decrease in its strength, without significantly adversely affecting the capacity of the composite system. Details of when to fill the voids are widely available. They are given in SCI P359 and also in the Yellow Book[13].
[top]External steelwork in fire
Main articles: Structural fire engineering
Modern steel framed buildings are sometimes constructed with the structural frame on the outside of the facade. Since, in the event of a fire, an external structural frame will be heated only by flames emanating from windows or other openings in the building facade, the fire that the external steelwork experiences may be less severe than that to which the steel inside the building is exposed.
It may be possible to design the frame members to remain unprotected or to have reduced protection if they are positioned so that they will not be engulfed by flames and hot gases issuing from facade openings. Assessment can be carried out in accordance with SCI P375. This describes the calculation process involved in determining the temperatures reached by external steel subject to a fire in an adjacent compartment. It involves calculation of: the flame velocity; the flame height above the window; the horizontal flame projection; the effective flame temperature; the flame emissivity; the configuration factor for the flame with respect to the steel the effective fire temperature; the configuration factor for the openings with respect to the steel; and the rate of burning within the compartment.
BS EN 1993-1-2[2] Appendix B also contains a method for calculation of the size and temperature of flames from openings and radiation and convection parameters for heat transfer calculations.
Where external steel is not required to be aesthetic and/or it requires resistance to damage and abrasion, concrete encasement is still sometimes used as a form of fire protection. Some spray protection materials can also be used and may also be suitable for situations where the risk is from hydrocarbon fires.
The most common form of fire protection used on external steel is thin film intumescent coating. It should be recognised that there will be a limit on the time for which the manufacturers will guarantee the performance of their materials. Care should always be taken to ensure that the manufacturers’ application specification is followed so that the performance guarantee is valid.
In addition, thick film epoxy intumescents are used to fire protect external steel. A case study is available here. These are also available as precast products.
A case study on an engineered solution for external steel in fire is available by following the link here
[top]Car parks in fire
Main articles: Car parks in fire, Calculating section factors
For the purposes of fire resistance, car parks for light vehicles can be classed as either open sided, or all other types. Approved Document B[3] defines the requirements for open sided car parks. Open car parks can be considered as a special case of external steelwork. In the UK, the authorities recognise that there is a low risk of fire spread and ample opportunity for smoke and hot gases to be dissipated in open car parks when certain ventilation criteria are met. Therefore fire resistance requirements are low and the steel frame is generally unprotected as long as defined section factor requirements are also met.
The fire resistance requirements for other car parks are typically consistent with those for commercial buildings of the same height.
[top]Single storey buildings in fire
Main articles: Single storey buildings in fire boundary conditions
In the UK, structural frames in single storey buildings do not normally require fire protection. Approved Document B[3], Section 7.3, excludes from the definition of elements of structure, that structure which only supports a roof. This is because the provisions of the Building Regulations exist mainly for the purposes of life safety and fires in single storey buildings are not generally considered to pose a significant threat in that regard.
Fire resistance is required when single storey non-domestic buildings are located close to a boundary. The objective is to stop fire spreading to adjacent buildings. The Building Regulations define when a building falls within the scope of a boundary condition
Where a single storey building exists in a boundary condition, it has been widely accepted that it is necessary only for the affected elevation and its supporting steel columns to be fire protected. The rafters may be left unprotected but the column base must be designed to resist the overturning moment caused by the collapse of the unprotected parts of the building in fire. The method of calculation used to derive the horizontal forces and moments created by rafter collapse is given in SCI P313; this is referenced in Section 13.15 of Approved Document B[3] and Section 2.D.2 of Scottish Technical Handbook 2022[5].
[top]Active fire protection
Main articles: Sprinklers in UK fire codes
Sprinklers are designed to suppress automatically small fires on, or shortly after, ignition or to contain fires until the arrival of the fire service. In England Approved Document B[3] requires that almost all buildings over 30 metres in height are required to have an approved life safety sprinkler system installed. A reduction of 30 minutes in the required fire resistance may be applied to many types of occupancies less than 30 metres in height when a life safety sprinkler system is installed and other concessions are also possible. Technical Booklet E[6] addresses the issue in a similar way.
In the special case of large shopping complexes, Approved Document B[3] requires that the provisions of BS 9999[7] are followed for fire precautions and this usually means that a life safety sprinkler system is installed for any covered shopping complex.
In Scottish Technical Handbook 2022[5], sprinklers are not mandatory in most buildings, with the following exceptions: enclosed shopping centres; residential care buildings; sheltered housing complexes, school buildings ; a building containing flats or maisonettes; social housing and shared multi-occupancy residential buildings.
BS 9999[7] also allows concessions for sprinklers. In general, these are more attractive than those on offer in Approved Document B[3] and can affect issues such as structural fire resistance, maximum travel distances and minimum door widths.
[top]Structural fire engineering
Main articles: Structural fire engineering
Increasing innovation in design, construction and usage of modern buildings has created a situation where it is sometimes difficult to satisfy the functional requirements of the Building Regulations by the use only of the provisions given in Approved Document B[3], Scottish Technical Handbook 2022 [5] and Technical Booklet E[6]. Recognition of this, and also increased knowledge of how real buildings react in fire and of how real fires behave, has led many authorities to acknowledge that improvements in fire safety may now be possible in many instances by adopting a comprehensive analytical and engineering approach to the particular structure and risks. This has been supported by a wide ranging and intensive programme of research and development world-wide. Thus Approved Document B[3] states that: Fire safety engineering can provide an alternative approach to fire safety. It may be the only practical way to achieve a satisfactory standard of safety in some large and complex buildings and in buildings containing different uses.
Fire safety engineering can be seen as an integrated package of measures designed to achieve the maximum benefit from the available methods of preventing, controlling or limiting the consequences of fire. The Institution of Structural Engineers says of structural fire engineering: By adopting a performance based approach to structural fire engineering….more economic designs can be achieved and more innovative and complex buildings can be constructed[16].
The move from prescriptive to functional requirements in the Building Regulations in the United Kingdom provided a huge boost to the development of fire engineering. As a consequence, the majority of tall and complex buildings now benefit from an engineered approach to fire rather than relying on the prescriptive provisions of Approved Document B[3] or similar. This has proved beneficial to the construction industry as a whole, but particularly to the steel construction sector, which has carried out most of the research and whose structures consequently offer the greatest potential for improved solutions using fire engineering.
An example of fire engineering is the consideration of localised fires rather than assuming that the temperature of an entire compartment within a building rises uniformly. Undertaking a performance-based fire engineering approach for certain types of structures such as airports and other large open buildings will produce a more accurate and more economic design. The analysis involves an assessment of the material that may cause the fire, the size and ventilation characteristics of the compartment and is considerably more complex than following a prescriptive approach. Guidance on the effect of localised fires on columns is given in SCI P423.
[top]Structural steel after fire
Main Articles: Design using structural fire standards, Fire damage assessment of hot rolled structural steelwork
Fire will affect structural steel and the extent of the impact needs to assessed once the fire has been extinguished. On many occasions steelwork exposed to fire shows little or no distortion, and this leads to uncertainty as to how it has been affected. This is particularly true in situations where fire has resulted in some parts of the structure exhibiting little or no damage alongside areas where considerable damage and distortion are clearly visible.
All materials weaken with increasing temperature and steel is no exception. Strength loss for steel is generally accepted to begin at about 300°C and increases rapidly after 400°C. By 550°C the most common grades of hot rolled structural steel retain about 60% of their room temperature yield strength. This is often considered to be the failure temperature for structural steel, but in practice this is a very conservative assumption - the calculated failure temperature may be significantly higher.
Structural steels that are heated above 600°C will lose some of their properties on cooling. The extent of this loss is a function of the grade of steel, with the higher grades being most affected. Tests exist to check if any such loss of properties has taken place.
Fires can also cause distortion and yielding in bolts and connections due to thermal expansion and contraction. Checks should always be carried out to determine if this has led to weld cracking, bolt shearing etc.
Detailed information is available on the reinstatement of steel after fire in the publication The Reinstatement of Fire Damaged Iron and Steel Framed Structures.
[top]References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 BS 5950-8: 2003, Structural use of steelwork in buildings. Code of practice for fire resistant design. BSI
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 BS EN 1993-1-2: 2005, Design of steel structures. General rules - structural fire design. BSI
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 Approved Document B (Fire safety, Volume 2 – Buildings other than Dwellings), 2019 edition incorporating 2020 amendments – for use in England . Ministry of Housing, Communities & Local Government
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Approved Document B, Volume 2 – Buildings other than dwellinghouses, Fire safety, 2006 Edition incorporating 2010, 2013, 2016, 2017 and 2020 amendments - For use in Wales*, Welsh Government
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Building standards technical handbook: 2022 – Non-domestic, Section 2 – Fire, The Scottish Government
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Technical Booklet E, Fire safety, Building Regulations (Northern Ireland) 2012, Department of Finance and Personnel of the Northern Ireland Government, 2012
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 BS 9999: 2017, Fire safety in the design, management and use of buildings - Code of practice. BSI
- ↑ BS 476-20: 1987, Fire tests on building materials and structures. Method for determination of the fire resistance of elements of construction (general principles). BSI
- ↑ ISO 834-1: 1999, Fire-resistance tests - Elements of building construction. General requirements. International Standards Organisation
- ↑ BS EN 1363-1: 2020, Fire resistance tests. General requirements . BSI
- ↑ BS EN 1991-1-2: 2002, Actions on Structures. General actions - Actions on structures exposed to fire. BSI
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 BS EN 1994-1-2: 2005+A1:2014, Design of composite steel and concrete structures. General rules. Structural fire design. BSI
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Fire protection for structural steel in buildings. Volume 1 6th edition. Association for Specialist Fire Protection
- ↑ BS EN 1994-1-1:2004. Design of composite steel and concrete structures. General rules and rules for buildings BSI
- ↑ BS 5950-4: 1994, Structural use of steelwork in building. Code of practice for design of composite slabs with profiled steel sheeting, BSI
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Guide to the advanced fire safety engineering of structures. Institution of Structural Engineers, 2007
[top]Resources
- Steel Construction - Fire Protection Supplement, 2024
- Steel construction - Fire Protection supplement, 2013
- SCI P056 The Fire Resistance of Composite Floors with Steel Decking, 2nd ed.
- SCI P080 Fire resistant design of steel structures – A handbook to BS 5950 Part 8, 1990
- SCI P113 Structural fire engineering: Investigation of Broadgate Phase 8 fire
- SCI P124. The fire resistance of web-infilled steel columns, 1992
- SCI P126 The fire resistance of shelf angle floor beams to BS5950 Part 8, 1993
- SCI P186 Design of Steel Framed Buildings without Applied Fire Protection, 1999
- SCI P259 The Fire Resistance of Concrete Filled Tubes to Eurocode 4, 2000
- SCI P313, Single Storey Steel Framed Buildings in Fire Boundary Conditions
- SCI P359 Composite Design of Steel Framed Buildings, 2011
- SCI P363 Steel Building Design: Design Data, 2013
A web-based interactive version of the 'Blue Book', is also available. - SCI P375 Fire Resistance Design of Steel Framed Buildings
- SCI P403 Resistance of beams & columns in fire: Worked examples to the Eurocodes, 2014
- SCI P423 Design of columns subject to localised fires, 2018
- SCI P424 Fire resistance of Light Steel Framing, 2021
- SCI P429 Fire Resistance to Steel Sections Galvanized to EN ISO 1461, 2020
- The Reinstatement of Fire Damaged Iron and Steel Framed Structures
- NCCI: PN006a-GB Design of reinforced, concrete filled, hot finished structural steel hollow sections in fire
- Design example for the calculation of critical temperatures for beams and columns in a two storey building
- Design example for the calculation of critical temperatures for beams and columns in a seven storey building
Member fire design tools:
- Resistance of beams at elevated temperature
- Resistance of columns at elevated temperature
- Composite Beam Checking Tool
[top]See also
- Calculating section factors
- Car parks in fire
- Design using structural fire standards
- Design of composite steel deck floors for fire
- Eurocode classification of sections in fire
- Fire damage assessment of hot rolled structural steelwork
- Fire protecting structural steelwork
- Fire testing
- Single storey buildings in fire boundary conditions
- Sprinklers in UK fire codes
- Structural fire engineering
- Structural fire resistance requirements
- Hollow sections in fire